For more than two decades, the 100-meter limit has been a cornerstone of Ethernet networking over twisted pair copper cabling. This 100-meter standard, established in the late 1990s, has served the industry well, providing a reliable benchmark for network design and implementation. However, as technology advances and network demands evolve, there's growing interest in pushing beyond this traditional boundary.
Pushing boundaries isn’t new for us. In recent history, we were at the forefront of developing and standardizing 28 AWG patch cords and field terminated plugs/modular plug terminated links – both well before standards were modified to make those solutions part of a standards-defined channel. However, while we are willing to push the boundaries, the result must preserve the reliability of the channel. After all, if the solution doesn’t reliably deliver data and power once it’s installed, then what’s the point?
We recently turned our attention to cabling solutions that would meet demands for a channel longer than 100 meters. After extensive research conducted by Panduit engineers at the Jack E. Caveney Innovation Center, we have published a white paper, "Beyond the Standards: Extending the Reach of Copper Cabling." The paper explores the feasibility and reliability of extending 1000BASE-T Ethernet connections beyond the standard 100-meter limit using advanced copper cabling technologies.
The Challenge of Extended Reach
The 100-meter limit defined in ANSI/TIA-568.2-D isn’t arbitrary; it represents a calculated maximum distance that ensures reliable data transmission under the original Category 5 cabling specifications. As the industry pushes to extend this reach, several critical factors come into play:
- Signal degradation over longer distances
- Increased noise and interference
- Propagation delay and delay skew
- Compatibility with existing network equipment
The Panduit research team, led by Paul Wachtel, tackled these challenges, leveraging the improved performance characteristics of newer cabling categories and larger gauge conductors.
Key Findings
The paper reveals several crucial insights:
- Category 6 and Category 6A Advantages: These newer cabling standards offer significant improvements in insertion loss, near-end crosstalk (NEXT), and return loss compared to Category 5. This enhanced performance provides additional margin for signal integrity over longer distances.
- 22 AWG Cabling Benefits: Utilizing larger 22 AWG conductors in horizontal cabling further reduces insertion loss and DC resistance, contributing to improved signal strength at extended lengths.
- Reliable Extended Reach: Panduit testing demonstrated that a point-to-point distance of 150 meters can reliably support 1000BASE-T Ethernet connections.
- Performance Validation: The 150-meter channel was thoroughly tested using industry-standard methods, including the Enhanced RFC 2544 benchmark test. Results showed no throughput degradation and zero frame loss across a diverse range of networking equipment.
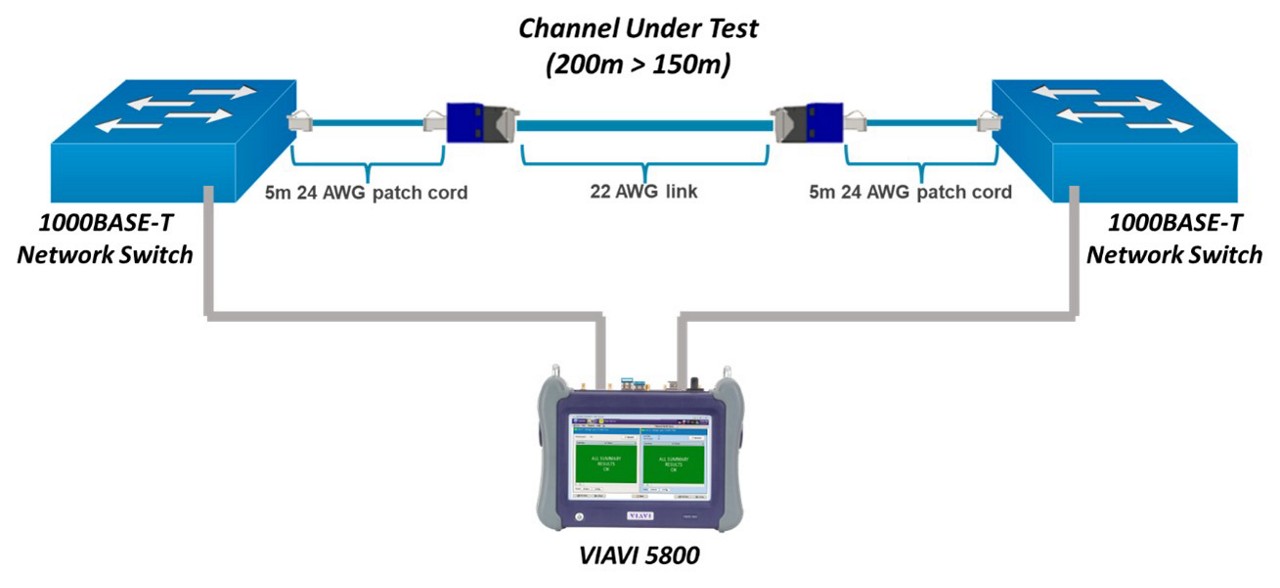
The 150-meter channel was thoroughly tested using a variety of industry-standard methods.
5. PoE Compatibility: The extended reach solution also supports Power over Ethernet applications, meeting key requirements for DC resistance and resistance unbalance.
6. Limitations Beyond 150 Meters: While some industry claims suggest 1000BASE-T communication up to 200 meters, our research indicates significant risks and reliability issues beyond the 150-meter mark.
Implications for Network Design and Implementation
This research opens new possibilities for network architects and installers. The ability to extend Ethernet connections to 150 meters without sacrificing performance can have substantial benefits when connecting to security cameras, wireless access points, or access control systems such as building entrances or parking lot gates that are beyond the 100-meter limit. Running extended reach cabling eliminates the need for an additional IDF, extender, or other components that can be more complex to install and more costly.

Network-connected devices that are positioned more than 100 meters from the nearest TR are prime candidates for extended reach cabling.
Other scenarios where extended reach cabling is beneficial:
- Large industrial facilities where equipment may be spread over greater distances
- Campus environments with buildings located beyond the traditional 100-meter limit
- Retrofitting older buildings with centralized network closets
- Temporary installations for events or construction sites
However, it's important to note that an extended reach solution requires careful consideration and proper implementation. The use of high-quality 22 AWG Category 6 or Category 6A cabling is essential, as is adherence to best practices in installation and testing.
Our Commitment to Reliability
Based on our research and testing, we are confident about our 22 AWG solution and are backing that with the Panduit Certification Plus℠ Warranty for 1000BASE-T performance on channels up to 150 meters in length, provided they meet the specific parameters outlined in the white paper and are installed according to warranty guidelines.
This warranty underscores our commitment to pushing the boundaries of network infrastructure while maintaining the highest standards of reliability and performance.
Conclusion
The ability to extend Ethernet's reach to 150 meters represents a significant advancement in network infrastructure technology. It offers new flexibility in network design without compromising on the performance and reliability that modern businesses depend on.
However, as with any cutting-edge technology, proper implementation is key. Network professionals should thoroughly understand the requirements and limitations of extended reach solutions before incorporating them into their designs.
We encourage you to download and read the full white paper, "Beyond the Standards: Extending the Reach of Copper Cabling." This comprehensive document provides in-depth technical analysis, detailed test results, and valuable insights that can help you make informed decisions about implementing extended reach Ethernet in your network infrastructure projects.
By staying informed about these advancements and understanding their practical applications, you can ensure that your network infrastructure is not only meeting today's needs but is also prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.
Download the full white paper now to dive deeper into the future of extended reach Ethernet and discover how it can benefit your network infrastructure projects.


